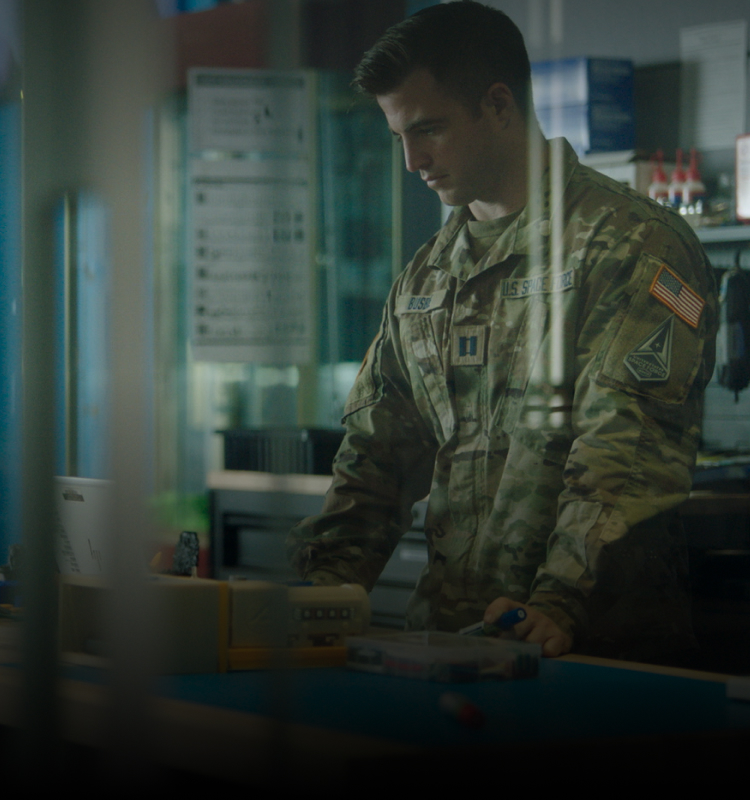

About
Many of the questions you have about the Space Force have been asked before. Explore our Frequently Asked Questions to learn more.
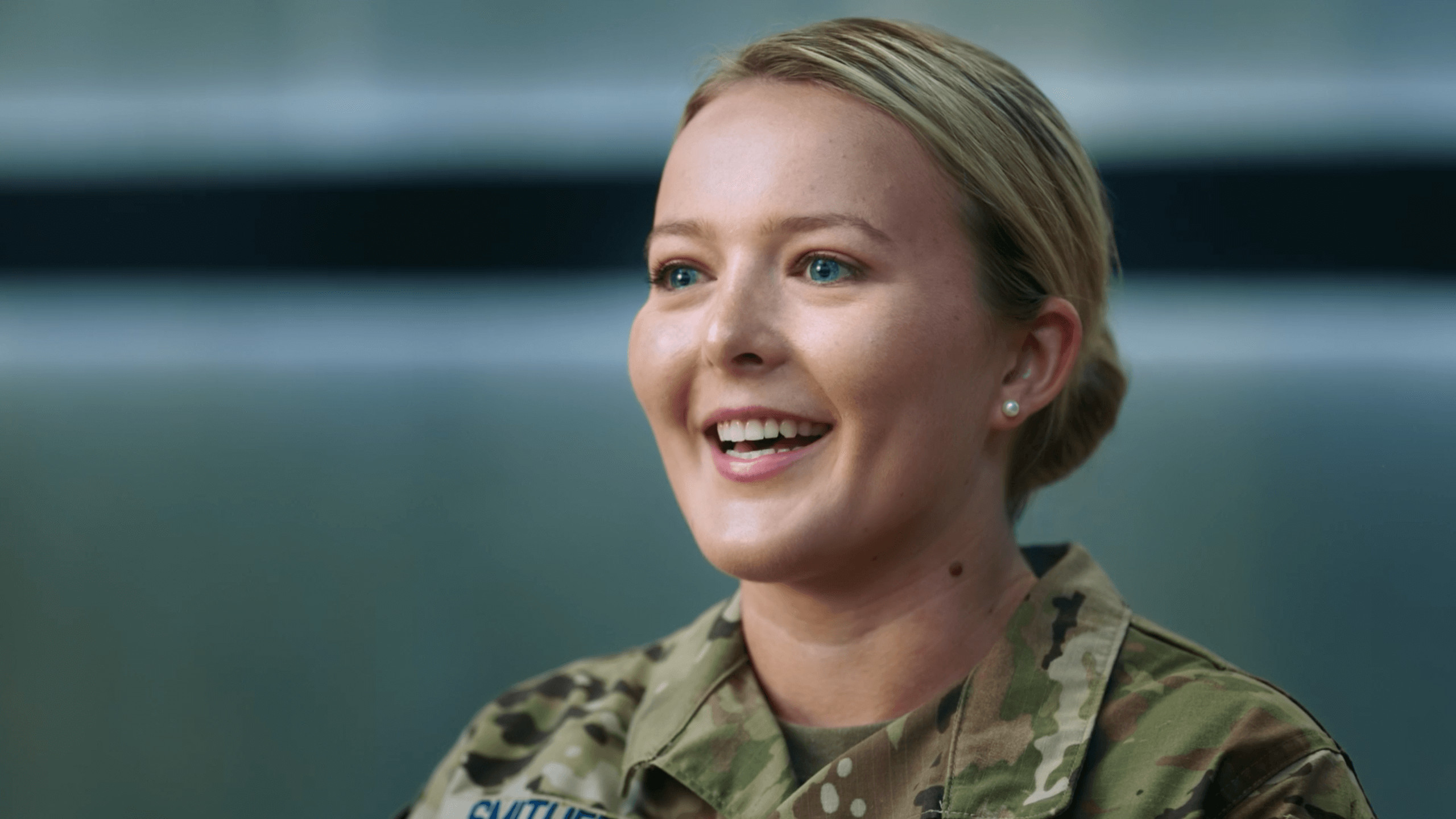

Learn more about what we do and why we serve.
Some think we're astronauts and we work on spaceships, but that's far from the case. From space to cyberspace, our reach is global and our duties protect our everyday way of life. You just don't see them.
The U.S. Space Force’s mission is to secure our nation’s interests in, from, and to space. The USSF is responsible for organizing, training and equipping Guardians to conduct global space operations that enhance the way our joint and coalition forces fight, while also offering decision makers military options to achieve national objectives.
Both organizations work to improve our capabilities in space but with different directives. NASA is a civil agency that focuses on developing resources for education, exploration, innovation and research, while Space Force is a military service centered around the vital capabilities needed to defend the United States’ interests and freedom to operate in space.
The Space Force trains, organizes and equips Guardians to perform global space operations that improve how our joint services fight, communicate and achieve national objectives. These operations include developing and defending communication satellites, engineering global cybersecurity networks, supporting rocket launches, tracking space debris and coordinating battlefield operations across all war-fighting domains.
The Space Force was established on December 20, 2019 as part of the National Defense Authorization Act.
The Space Force consists of approximately 9,400 Active Duty Guardians.
The term “Guardians” has a long history in space operations, tracing back to the Air Force Space Command’s (AFSPC) motto in 1983, “Guardians of the High Frontier.” This name strongly connects our culture and heritage to our mission to protect our country and its freedom to operate in space.
Unlike other military branches, the Space Force does not have a national guard or reserve component. It consists of only full-time enlisted, officer and civilian personnel.